Synonyms: Propanedioic acid
Cas No. 141-82-2
Molecular Weight: 104.6
Description:
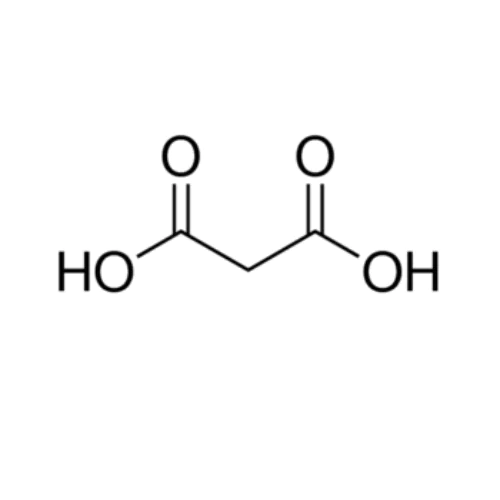
Malonic acid also known as propanedioic acid is a dicarboxylic acid. It is a colorless, crystalline solid that is water-soluble. Malonic acid contains two carboxyl groups (-COOH) attached to a three-carbon chain. Its structure can be represented as HOOC-CH₂-COOH.
Key Characteristics and Uses:
- Structure: The IUPAC name is propanedioic acid, which reflects its three-carbon backbone with two carboxyl groups.
- Synthesis: Malonic acid is commonly produced by the cyanoacetic acid method or by hydrolysis of cyanide compounds.
- Uses:
- In Organic Synthesis: It serves as a building block in the production of various chemicals, including barbiturates and certain pharmaceuticals.
- In the Malonic Ester Synthesis: This is a method used to prepare acetic acids and other organic compounds, especially in the synthesis of substituted acetic acids.
- In Biochemistry: It can be involved in metabolic processes, such as the citric acid cycle, though it is not a central metabolite.
- Physical Properties:
- Melting point: 135 °C (275 °F)
- Boiling point: 135–140 °C (275–284 °F)
- Solubility: Soluble in water, ethanol, and ether.
- Toxicity: Like many organic acids, malonic acid should be handled with care, although it is generally considered less hazardous than other strong acids.
Specification:
Purity: 99%
Form: Powder or Crystals
Color: White


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.